Supernova 1987A
On February 23, 1987, a supernova was detected in the Large Magellanic Cloud about 160,000 light years from Earth. The first supernova to be discovered that year, it was designated 1987A.
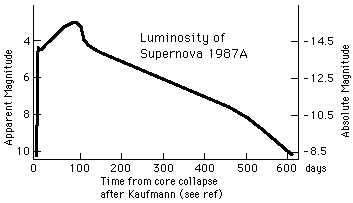 |
Reaching an apparent magnitude of about 3, it could easily be seen with the naked eye, the brightest such event since 1604. Since its distance from the Earth is known, its absolute magnitude could be calculated.
|
Supernova concepts
Reference
Kaufmann
