Light Absorption for Photosynthesis
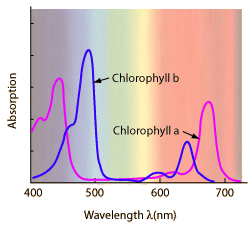 | Photosynthesis depends upon the absorption of light by pigments in the leaves of plants. The most important of these is chlorophyll-a, but there are several accessory pigments that also contribute. |
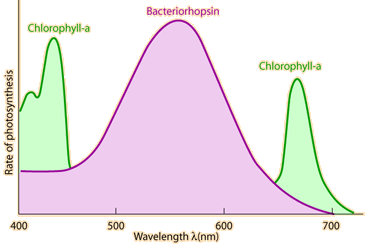
The measured rate of photosynthesis as a function of absorbed wavelength correlates well with the absorption frequencies of chlorophyll a, but makes it evident that there are some other contributors to the absorption. | 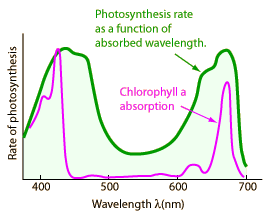 |
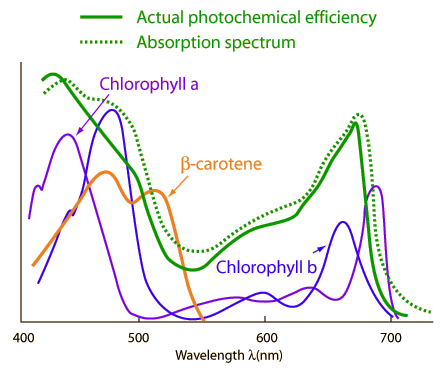
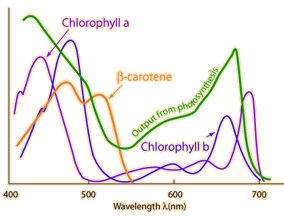
The plot of the absorption spectra of the chlorophylls plus beta carotene correlates well with the observed photosynthetic output. The measure of photochemical efficiency is made by meauring the amount of oxygen produced by leaves following exposure to various wavelengths.
It is evident from these absorption and output plots that only the red and blue ends of the visible part of the electromagnetic spectrum are used by plants in photosynthesis. The reflection and transmission of the middle of the spectrum gives the leaves their green visual color.
| Why are leaves not black? |
| Photosynthetic Efficiency |
| Energy cycle in living things |
Photosynthesis Concepts
Reference
Moore, et al.
Ch 7
Karp
Ch 6
| HyperPhysics***** Biology | R Nave |