Norton: Two Loop Problem
To apply Norton's Theorem to the solution of the two loop problem, consider the current through resistor R2 below. Replacing the remainder of the network by its Norton equivalent simplifies the determination of I2 .
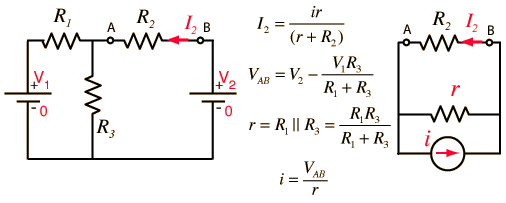
Note: To avoid dealing with so many short circuits, any resistor with value zero will default to 1 when a voltage is changed. It can be changed back to a zero value if you wish to explore the effects of short circuits. Ohms and amperes are the default units, but if you put in resistor values in kilohms, then the currents will be milliamperes.
| Other approaches to two-loop circuits |
DC Circuits