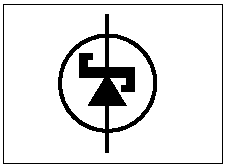
Varactor
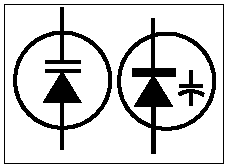 |
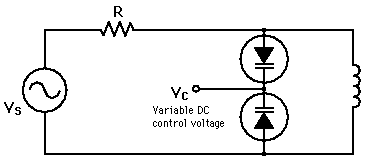
A varactor diode uses a p-n junction in reverse bias and has a structure such that the capacitance of the diode varies with the reverse voltage. A voltage controlled capacitance is useful for tuning applications. The capacitance is controlled by the method of doping in the depletion layer. Typical values are from tens to hundreds of picofarads. |
Electronics concepts
Diode varieties
| HyperPhysics*****Electricity and magnetism | R Nave |