Vergence
The vergence of light is defined by
where n is the index of refraction of the medium and L is the distance in accordance with the Cartesian sign convention.
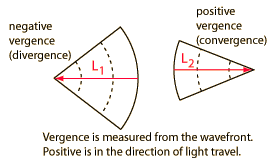 |
Since the distance L1 is measured from the wavefront and light is traveling left to right, it is a negative distance and the vergence is negative (divergent). L2 is positive since it is directed to the right from the wavefront (convergent). |
The change in vergence when the light encounters a refracting surface is equal to the power of the surface Ps:
| Vergence Example | Vergence Tracing in Thick Lenses |
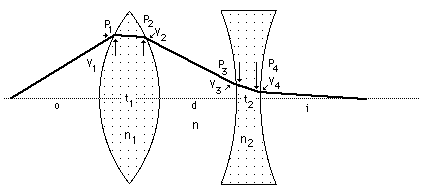
Lens concepts
Thick lens concepts
| HyperPhysics***** Light and Vision | R Nave |