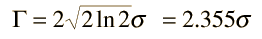Gaussian Distribution Function
| Distribution | Functional Form | Mean | Standard Deviation |
| Gaussian | 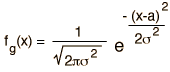 | 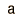 | 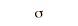 |
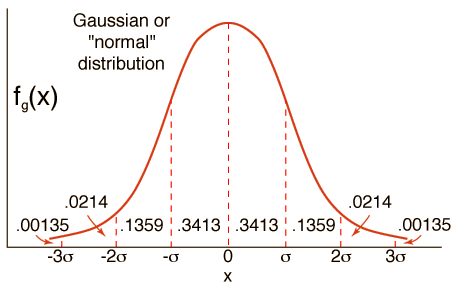
If the number of events is very large, then the Gaussian distribution function may be used to describe physical events. The Gaussian distribution is a continuous function which approximates the exact binomial distribution of events.
The Gaussian distribution shown is normalized so that the sum over all values of x gives a probability of 1. The nature of the gaussian gives a probability of 0.683 of being within one standard deviation of the mean. The mean value is a=np where n is the number of events and p the probability of any integer value of x (this expression carries over from the binomial distribution ). The standard deviation expression used is also that of the binomial distribution.
The Gaussian distribution is also commonly called the "normal distribution" and is often described as a "bell-shaped curve".
Show Gaussian curve
Distribution functions
Applied statistics concepts