RuBisCO
The enzyme ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase, most commonly known by the shorter name RuBisCO or just rubisco is used in the Calvin cycle to catalyze the first major step of carbon fixation. RuBisCO is thought to be the most abundant protein in the world since it is present in every plant that undergoes photosynthesis and molecular synthesis through the Calvin cycle. Moore, et al.'s summary includes the assessment that rubisco makes up 20-25% of the soluble protein in leaves and is made on the Earth at the rate of about 1000 kg/s. They estimate that every person on Earth is supported by about 44 kg of rubisco!
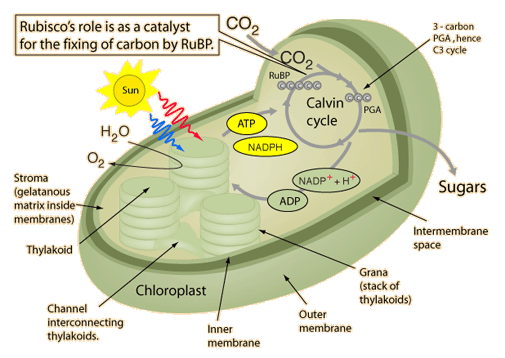
"RuBisCO catalyzes either the carboxylation or oxygenation of ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate (known as RuBP) with carbon dioxide or oxygen. What makes it unique and different to every other enzyme is the fact that it can survive on its own without the need of the plant so even if it is dead it remains and helps decomposition. This is due to it not being affected by temperature or pH. "(Wikipedia)
RuBisCo has a molecular weight of 490,000 Daltons and is composed of eight large subunits and eight small subunits. The large subunits are coded in the chloroplast itself, while the small units are coded in the nucleus of the cell.
| RuBisCO wiki |
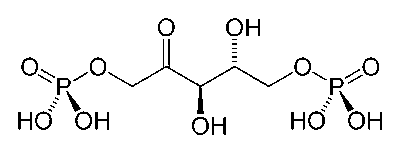
Organic chemistry concepts
Chemistry concepts
Reference
Karp
Ch 3
Moore, et al.
Ch 7
| HyperPhysics*****Chemistry | R Nave |