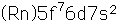Curium
Curium, a trans-uranic element, was first discovered by Glenn Seaborg and collaborators at the University of California, Berkeley.
Curium was made by bombarding plutonium-239 with helium nuclei which had been accelerated in the cyclotron. The capture of the helium nucleus and the emission of a neutron left the isotope curium-242. Cm-242 is an alpha emitter with a half-life of about five years. Another isotope, curium-240, has been produced by the same bombardment, where three neutrons are released in the interaction.
|
Index
Periodic Table
Chemistry concepts
Reference
Pauling
Ch. 29 |