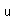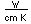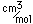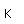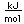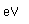Lutetium
As a member of the fourteen member lanthanide series, this element has few properties which distinguish it from the other members of the series. All of them along with lanthanum, yttrium, and scandium occur in very small quantities in nature. The usual source is the mineral monazite, or monazite sand, which is a mixture of phosphates containing also some thorium phosphate.
One notable thing about lutetium is that its nucleus is highly deformed, having one of the largest electric quadrupole moments of all nuclides. The quadrupole moment of the departure from spherical symmetry of the charge of the nucleus.
|
Index
Periodic Table
Chemistry concepts
Reference
Pauling
Ch. 26 |