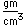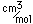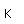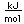Radon
Radon is a noble gas which is produced steadily by the radioactive decay of radium.
Radon is radioactive, and has been found useful in localized radiation therapy for cancer. Radon is pumped into a small gold tube, which is then placed at the center of the tissue to be treated. With it's 3.8 day halflife, the radiation diminishes rapidly and disposal is not a big problem. The gold capsule blocks the alpha emissions from the daughter products of radon, so that the gamma rays only are used therapeutically.
Radon has received a great deal of publicity as a possible long-term radiation hazard in some buildings where radon from the earth may enter the ground floor of the buildings.
|