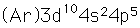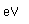Bromine
Bromine is an easily volatile, dark reddish-brown liquid with a strong disagreeable odor and an irritating effect on the eyes and throat. It produces painful lesions when spilled on the skin.
Hydrogen bromide, HBr, is a colorless gas. In solution with water it forms a strong acid, hydrobromic acid. Reaction with metals or metallic bases produces bromides such as sodium bromide, NaBr and potassium bromide, KBr which are used in medicine. The salt silver bromide, AgBr, is used for making photographic emulsions and appears naturally in the mineral bromargyrite.
Bromine occurs in the form of compounds in small quantities in sea water and in natural salt deposits. The element can be released from the bromides by treating them with a strong oxidizing agent such as chlorine.
|
Index
Periodic Table
Chemistry concepts
Reference
Pauling
Ch. 13 |