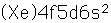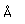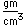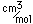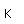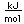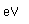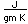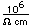Cerium
As a member of the fourteen member lanthanide series, this element has few properties which distinguish it from the other members of the series. All of them along with lanthanum, yttrium, and scandium occur in very small quantities in nature. The usual source is the mineral monazite, or monazite sand, which is a mixture of phosphates containing also some thorium phosphate. Minerals that contain cerium along with lanthanum are Parisite, bastnaesite, and allanite. Cerium is also found in the mineral hibonite. Cerium appears in the silicate mineral joaquinite and the oxide mineral euxenite.
An alloy of about 70% cerium and smaller amounts of the other lanthanons and iron has the property of giving off sparks when scratched. It is widely used in gas lighters and igniters.
Cerium monosulfide, CeS, is very hard and has a high melting temperature (2450°C), so it has found use in making refractory vessels.
Cerium has been used in the manufacture of mantles for gas lanterns. The fabric of the mantles is saturated with thorium nitrate and cerium nitrate. The burning of the mantles leaves a residue of thorium and cerium dioxides. This residue glows with a brilliant white luminescence when heated to a high temperature by the gas flame. The presence of the thorium makes these mantles slightly radioactive, so recent mantles have replaced these oxides with other illuminants.
|
Index
Periodic Table
Chemistry concepts
Reference
Pauling
Ch. 26 |