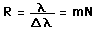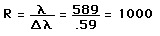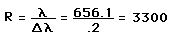Resolvance of Grating
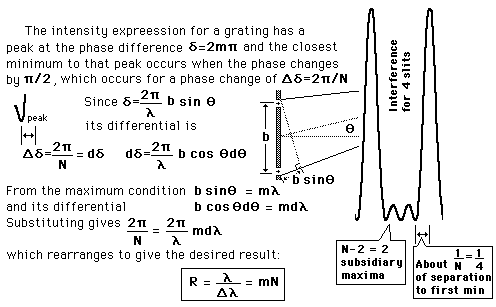
Resolvance or "chromatic resolving power" for a device used to separate the wavelengths of light is defined as

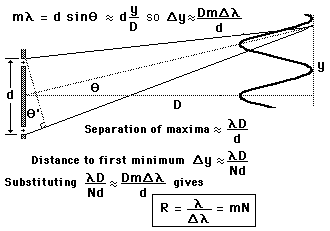
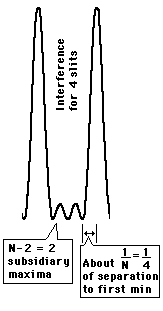
The limit of resolution is determined by the Rayleigh criterion as applied to the diffraction maxima, i.e., two wavelengths are just resolved when the maximum of one lies at the first minimum of the other.
Since the space between maxima for N slits is
broken up into N-2 subsidiary maxima, the
distance to the first mimimum is essentially
1/N times the separation of the main maxima.
This leads to a resolvance for a grating of
where N is the total number of slits illuminated and m is the order of the diffraction. |
 |
Grating concepts
| HyperPhysics***** Light and Vision | R Nave |