Second Law of Thermodynamics
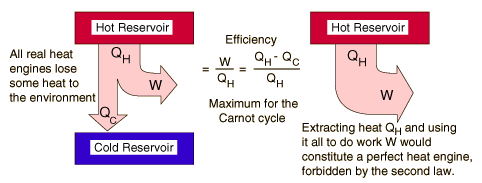
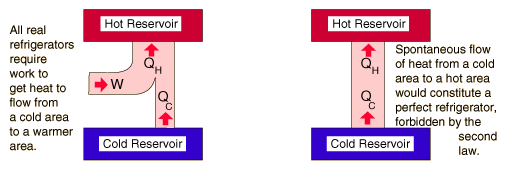
| The second law of thermodynamics is a general principle which places constraints upon the direction of heat transfer and the attainable efficiencies of heat engines. In so doing, it goes beyond the limitations imposed by the first law of thermodynamics. It's implications may be visualized in terms of the waterfall analogy. |
|

The maximum efficiency which can be achieved is the Carnot efficiency.
| Qualitative statements of the Second Law of Thermodynamics |
Second law concepts
Heat engine concepts
| HyperPhysics***** Thermodynamics | R Nave |