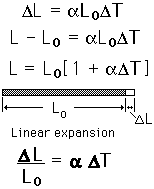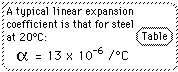Thermal Expansion
Over small temperature ranges, the linear nature of thermal expansion leads to expansion relationships for length, area, and volume in terms of the linear expansion coefficient .

| Table of expansion coefficients |
Expansion concepts
| HyperPhysics***** Thermodynamics | R Nave |