Torque
A torque is an influence which tends to change the rotational motion of an object. One way to quantify a torque is
Torque = Force applied x lever arm
The lever arm is defined as the perpendicular distance from the axis of rotation to the line of action of the force.
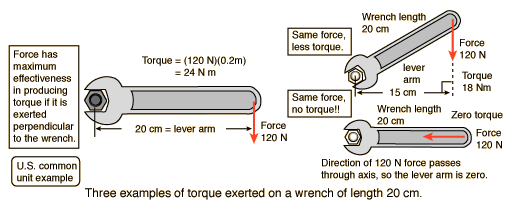
| Torque calculation |
| Torque expressions: | Trigonometric | Vector Product |
Rotation concepts
Torque concepts
| HyperPhysics***** Mechanics ***** Rotation | R Nave |

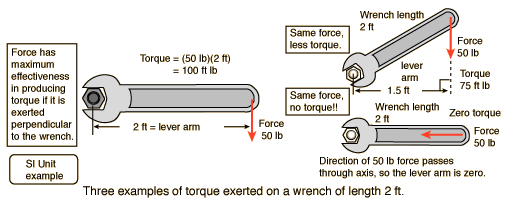 OK, this is a ridiculously large wrench. But it makes the numbers easy.
OK, this is a ridiculously large wrench. But it makes the numbers easy.