Rainbow Light Paths
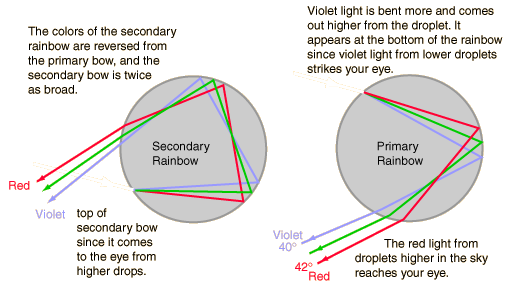
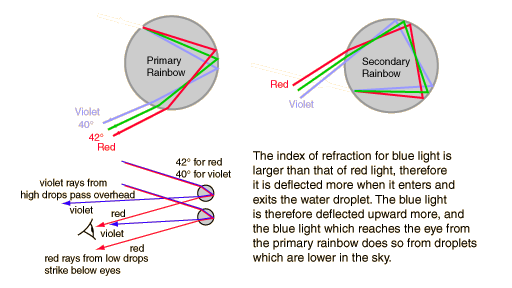
The light paths associated with the primary and secondary rainbows give insight into the formation of rainbows and the order of the colors. For the primary rainbow, the light is bent by refraction upon entering a water droplet, then reflected off the back of the droplet and refracted a second time as it exits the droplet.

| More detail | Rainbow image |
| Why is the blue lower than the red in a primary rainbow? |
| Why are the colors reversed in the secondary rainbow? |
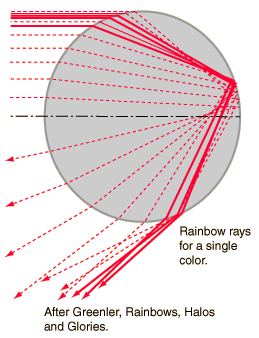
| Show the different paths for a single color |
Rainbow concepts
Atmospheric optics concepts
References
Greenler
Schaaf
| HyperPhysics***** Light and Vision | R Nave |