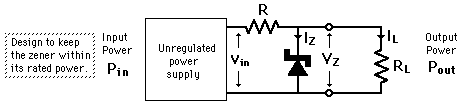
Zener Regulator
The constant reverse voltage 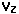 of the zener diode makes it a valuable component for the regulation of the output voltage against both variations in the input voltage from an unregulated power supply or variations in the load resistance. The current through the zener will change to keep the voltage at within the limits of the threshold of zener action and the maximum power it can dissipate.
of the zener diode makes it a valuable component for the regulation of the output voltage against both variations in the input voltage from an unregulated power supply or variations in the load resistance. The current through the zener will change to keep the voltage at within the limits of the threshold of zener action and the maximum power it can dissipate.
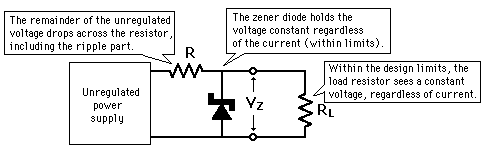
| Design Example | Buffer for Zener regulator |
Electronics concepts
Diode varieties
| HyperPhysics*****Electricity and magnetism | R Nave |