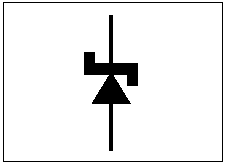
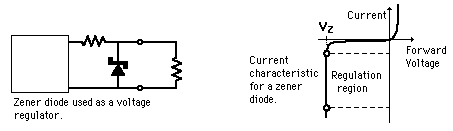
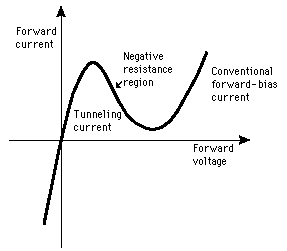
The Zener Effect
With the application of sufficient reverse voltage, a p-n junction will experience a rapid avalanche breakdown and conduct current in the reverse direction. Valence electrons which break free under the influence of the applied electric field can be accelerated enough that they can knock loose other electrons and the subsequent collisions quickly become an avalanche. When this process is taking place, very small changes in voltage can cause very large changes in current. The breakdown process depends upon the applied electric field, so by changing the thickness of the layer to which the voltage is applied, zener diodes can be formed which break down at voltages from about 4 volts to several hundred volts.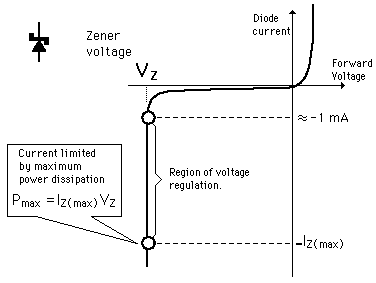
| Zener applications | Zener diode | zener regulator |
Semiconductor concepts
Semiconductors for electronics
Electronics concepts