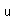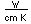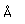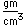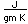Fluorine
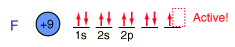
Fluorine, the lightest of the halogens, is the most reactive of all the elements. It forms compounds with all the elements except the noble gases.
The reactivity of pure fluorine gas is remarkable. Ordinary substances like wood and rubber burst into flame when held into a stream of fluorine. Even asbestos reacts so vigorously that it becomes incandescent. Copper and steel are attacked by it, but become coated with a thin layer of copper fluoride or iron fluoride and resist further attack. Steel tanks can therefore be used as containers for transport of fluorine.
Fluorine occurs in nature in minerals such as fluorite, CaF2, which can produce gem quality crystals. Fluorite is used to manufacture steel and is the main source of fluorine for toothpaste, fluoridated water, coolants, and Teflon. Also occurring as a mineral is fluorapatite, Ca5(PO4)3F, which is a constituent of bones and teeth. A small percentage of fluorapatite along with the more abundant calcium phosphates in teeth can make them more resistant to decay. Fluorine is found in the phosphate minerals Herderite and montebrasite.
Fluorine is contained in the silicate minerals carletonite, lepidolite, phlogopite, chondrodite, clintonite and fluorapophyllite.
Aluminum with boron and fluorine form the oxide (borate) Jeremejevite. Fluorine is found with calcium, solium and tantalum in the oxide mineral microlite.
Fluorine is in the sulfate mineral
creedite and the fluoride cryolite.
Lead with chlorine and fluorine form matlockite.
Fluorine is found with lanthanum and cerium in the carbonate mineral parisite.
Hydrogen fluoride, HF, in water is called hydrofluoric acid. It and the vapor phase HF can be used for etching glass. Hydrofluoric acid must be handled with great care, because skin contact produces lesions which heal very slowly. Hydrofluoric acid can be stored in polyethylene containers.
Reaction with the alkali metals produces salts called fluorides. Sodium fluoride, NaF, is used as an insecticide.
|