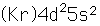Zirconium
Zirconium occurs in nature principally as a silicate mineral zircon, ZrSiO4. It is a hard mineral found in a variety of colors (white, blue, red, green) and is used as a semi-precious stone in jewelry. It also occurs in the silicates catapleiite and elpidite.
Another mineral form is the carbonate mineral Weloganite.
Zirconium appears with boron in the oxide mineral painite, which is very hard (MH =8) and sometimes of gem quality.
|
Index
Periodic Table
Chemistry concepts
Reference
Pauling
Ch. 29 |