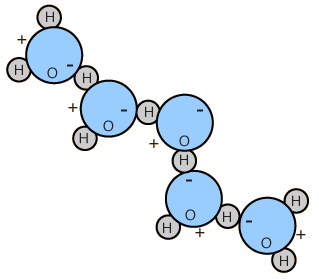
Dipole Moment of Water
|
The asymmetry of the water molecule leads to a dipole moment in the symmetry plane pointed toward the more positive hydrogen atoms. The measured magnitude of this dipole moment is 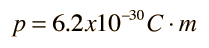 Treating this system like a negative charge of 10 electrons and a positive charge of 10e, the effective separation of the negative and positive charge centers is 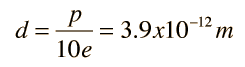 |
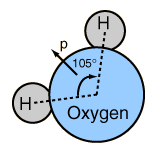 |
This is 0.0039 nm compares with about .05 nm for the first Bohr radius of a hydrogen atom and about .15 nm for the effective radius of hydrogen in liquid form, so the charge separation is small compared to an atomic radius.
The polar nature of water molecules allows them to bond to each other in groups and is associated with the high surface tension of water.
Voltage concepts
Electric dipole concepts
Reference
Halliday, Resnick, Walker
Sec 24.9
| HyperPhysics***** Electricity and Magnetism | R Nave |